![]() Ferrite Magnets Introduction
Ferrite Magnets Introduction

01. Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets Introduction
Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets are manufactured from oxide materials using powder metallurgical process. Ceramic magnet is most widely used because of its low cost, high-energy, good electric insulation and excellent resistance to demagnetization. The most common type of ceramic magnets are anisotropic strontium, anisotropic barium and isotropic barium magnet.
Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets are essentially composed of oxide materials with Barium Carbonate or Strontium Carbonate, manufactured under a powder metallurgical process. The feature of low recoil permeability, along with the high coercive force, makes them highly resistant to demagnetizing fields. In addition, their relatively low specific density and economical cost are also very attractive to the magnet designers.
When designing the ferrite magnets for a particular application, primary consideration should be given to its shape limitation due to the powder metallurgical manufacturing process and the temperature dependence of ferrite materials. Ferrite Magnets has good anti-corrosion performance, no surface treatment needed. At present, we have put our emphasis on the application for electric motors, magnetic separators, magnetic resonance imaging and automotive sensors.
Main products includes: hard ferrite arc or segment, ring magnets, rectangular magnets, ferrite power etc. Ferrite magnets have the following advatages: high coercive force, high electric resistance, long-time stability, and economical price. Meanwhile, we can manufacture new tools according to customers`demand.
02. Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets Production Process
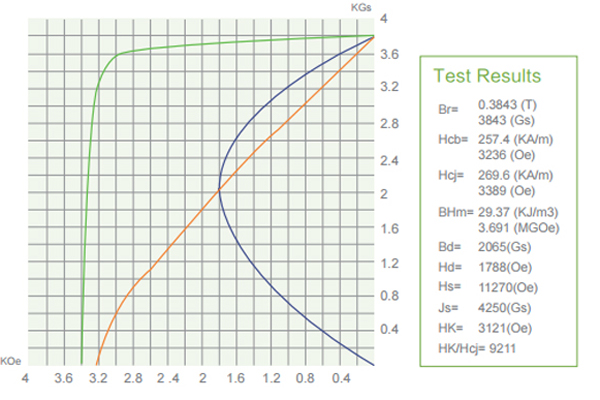
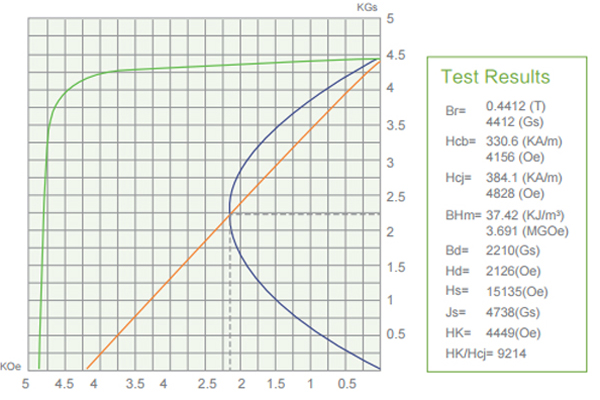
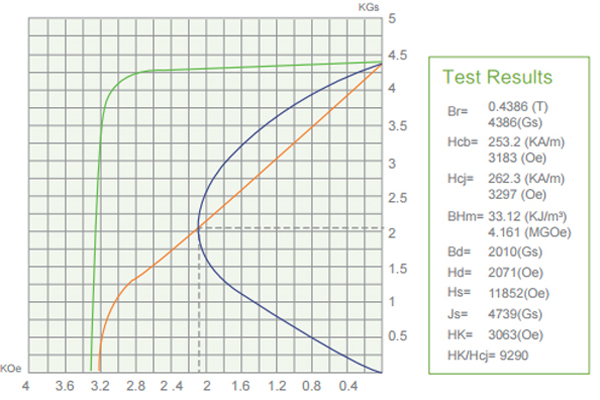
03. Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets Performance Datasheets
-
Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets Chinese Standard (SJ/T10410 2002) – commonly used globally, especially in UK and EU
| Grade | Remanence Br | Coercive Force Hcb | Intrinsic Coercivity Hcj | Max. Energy Product (BH)max | ||||
| mT | Gs | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | kOe | kJ/m³ | MGOe | |
| Y8T | 200-235 | 2,000-2,350 | 125-160 | 1.57-2.01 | 210-280 | 2.64-3.52 | 6.5-9.5 | 0.8-1.2 |
| Y22H | 310-360 | 3,100-3,600 | 220-250 | 2.76-3.14 | 280-320 | 3.52-4.02 | 20.0-24.0 | 2.5-3.0 |
| Y25 | 360-400 | 3,600-4,000 | 135-170 | 1.70-2.14 | 140-200 | 1.76-2.51 | 22.5-28.0 | 2.8-3.5 |
| Y26H-1 | 360-390 | 3,600-3,900 | 220-250 | 2.76-3.14 | 225-255 | 2.83-3.20 | 23.0-28.0 | 2.9-3.5 |
| Y26H-2 | 360-380 | 3,600-3,800 | 263-288 | 3.30-3.62 | 318-350 | 3.99-4.40 | 24.0-28.0 | 30-3.5 |
| Y27H | 350-380 | 3,500-3,800 | 225-240 | 2.83-3.01 | 235-260 | 2.95-3.27 | 25.0-29.0 | 3.1-3.6 |
| Y28 | 370-400 | 3,700-4,000 | 175-210 | 2.20-2.64 | 180-220 | 2.26-2.76 | 26.0-30.0 | 3.3-3.8 |
| Y28H-1 | 380-400 | 3,800-4,000 | 240-260 | 3.01-3.27 | 250-280 | 3.14-3.52 | 27.0-30.0 | 3.4-3.8 |
| Y28H-2 | 360-380 | 3,600-3,800 | 271-295 | 3.40-3.71 | 382-405 | 4.80-5.09 | 26.0-30.0 | 3.3-3.8 |
| Y30H-1 | 380-400 | 3,800-4,000 | 230-275 | 2.89-3.45 | 235-290 | 2.95-3.64 | 27.0-32.5 | 3.4-4.1 |
| Y30H-2 | 395-415 | 3,950-4,150 | 275-300 | 3.45-3.77 | 310-335 | 3.89-4.21 | 27.0-32.0 | 3.4-4.0 |
| Y32 | 400-420 | 4,000-4,200 | 160-190 | 2.01-2.39 | 165-195 | 2.07-2.45 | 30.0-33.5 | 3.8-4.2 |
| Y32H-1 | 400-420 | 4,000-4,200 | 190-230 | 2.39-2.89 | 230-250 | 2.89-3.14 | 31.5-35.0 | 4.0-4.4 |
| Y32H-2 | 400-440 | 4,000-4,400 | 224-240 | 2.81-3.01 | 230-250 | 2.89-3.14 | 31.0-34.0 | 3.9-4.3 |
| Y33 | 410-430 | 4,100-4,300 | 220~250 | 2.76-3.14 | 225-255 | 2.83-3.20 | 31.5-35.0 | 4.0-4.4 |
| Y33H | 410-430 | 4,100-4,300 | 250-270 | 3.14-3.39 | 250-275 | 3.14-3.45 | 31.5-35.0 | 4.0-4.4 |
| Y34 | 420-440 | 4,200-4,400 | 200-230 | 2.51-2.89 | 205-235 | 2.57-2.95 | 32.5-36.0 | 4.1-4.5 |
| Y35 | 430-450 | 4,300-4,500 | 215-239 | 2.70-3.00 | 217-242 | 2.73-3.04 | 33.1-38.2 | 4.2-4.8 |
| Y36 | 430-450 | 4,300-4,500 | 247-271 | 3.10-3.40 | 250-274 | 3.14-3.44 | 35.1-38.3 | 4.4-4.8 |
| Y38 | 440-460 | 4,400-4,600 | 285-305 | 3.58-3.83 | 294-310 | 3.69-3.89 | 36.6-40.6 | 4.6-5.1 |
| Y40 | 440-460 | 4,400-4,600 | 330-354 | 4.14-4.45 | 340-360 | 4.27-4.52 | 37.6-41.8 | 4.7-5.3 |
-
Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets USA Standard – also used in UK
| Grade | Remanence Br | Coercive Force Hcb | Intrinsic Coercivity Hcj | Max. Energy Product (BH)max | ||||
| mT | kGs | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | kOe | kJ/m³ | MGOe | |
| C1 | 230 | 2.30 | 148 | 1.86 | 258 | 3.50 | 8.36 | 1.05 |
| C5 | 380 | 3.80 | 191 | 2.40 | 199 | 2.50 | 27.00 | 3.40 |
| C7 | 340 | 3.40 | 258 | 3.23 | 318 | 4.00 | 21.90 | 2.75 |
| C8/C8A | 385 | 3.85 | 235 | 2.95 | 242 | 3.05 | 27.80 | 3.50 |
| C8B | 420 | 4.20 | 232 | 2.91 | 236 | 2.96 | 32.80 | 4.12 |
| C9 | 380 | 3.80 | 280 | 3.52 | 320 | 4.01 | 26.40 | 3.32 |
| C10 | 400 | 4.00 | 280 | 3.52 | 284 | 3.57 | 30.40 | 3.82 |
| C11 | 430 | 4.30 | 200 | 2.51 | 204 | 2.56 | 34.40 | 4.32 |
| C12 | 400 | 4.00 | 290 | 3.65 | 318 | 4.00 | 32.00 | 4.00 |
-
Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets Japan TDK standard
| Grade | Composition | Remanence Br | Coercive Force Hcb | Intrinsic Coercivity Hcj | Max. Energy Product (BH)max | ||||
| mT | kG | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | kOe | KJ/m3 | MGOe | ||
| FB40 | SrO6Fe2O3 | 410+/-10 | 4.1+/-10 | 234.8+/-11.9 | 2.95+/-0.15 | 238.7+/-15.9 | 3.0+/-0.2 | 31.4+/-1.6 | 3.95+/-0.2 |
| FB3N | SrO6Fe2O3 | 395+/-15 | 3.95+/-15 | 234.8+/-11.9 | 2.95+/-0.15 | 238.7+/-15.9 | 3.0+/-0.2 | 28.7+/-2.4 | 3.6+/-0.3 |
| FB3G | SrO6Fe2O3 | 375+/-15 | 3.75+/-15 | 254.6+/-15.9 | 3.2+/-0.2 | 270.6+/-19.9 | 3.4+/-0.25 | 25.9+/-2.4 | 3.25+/-0.3 |
| FB3X | SrO6Fe2O3 | 375+/-15 | 3.75+/-15 | 234.8+/-11.9 | 2.95+/-0.15 | 238.7+/-15.9 | 3.0+/-0.2 | 25.9+/-2.4 | 3.25+/-0.3 |
| FB1A | SrO6Fe2O3 | 220+/-15 | 2.20+/-15 | 159.2+/-15.9 | 2.0+/-0.2 | 258.6+/-19.9 | 3.25+/-0.25 | 8.9+/-1.6 | 1.1+/-0.2 |
| FB5H | SrO6Fe2O3 | 405+/-15 | 4.05+/-15 | 298.4+/-11.9 | 3.75+/-0.15 | 322.3+/-11.9 | 4.05+/-0.15 | 31.1+/-1.6 | 3.9+/-0.2 |
| FB4X | SrO6Fe2O3 | 420+/-10 | 4.20+/-10 | 234.8+/-11.9 | 2.95+/-0.15 | 238.7+/-15.9 | 3.0+/-0.2 | 33.4+/-1.6 | 4.2+/-0.2 |
| FB4B | SrO6Fe2O3 | 400+/-10 | 4.00+/-10 | 254.6+/-11.9 | 3.2+/-0.2 | 262.6+/-19.9 | 3.3+/-0.25 | 30.3+/-1.6 | 3.8+/-0.2 |
| FB4A | SrO/BaO6Fe2O3 | 410+/-10 | 4.10+/-10 | 175.1+/-15.9 | 2.2+/-0.2 | 176.7+/-15.9 | 2.22+/-0.2 | 31.8+/-1.6 | 4.0+/-0.2 |
| FBGN | SrO6Fe2O3 | 440+/-10 | 4.40+/-10 | 258.6+/-11.9 | 3.25+/-0.15 | 262.6+/-11.9 | 3.3+/-0.15 | 36.7+/-1.6 | 4.6+/-0.2 |
| FB6B | SrO6Fe2O3 | 420+/-10 | 4.20+/-10 | 302.4+/-11.9 | 3.8+/-0.15 | 318.3+/-11.9 | 4.0+/-0.15 | 33.4+/-1.6 | 4.2+/-0.2 |
| FB6H | SrO6Fe2O3 | 400+/-10 | 4.00+/-10 | 302.4+/-11.9 | 3.8+/-0.15 | 358.1+/-11.9 | 4.5+/-0.15 | 30.3+/-1.6 | 3.8+/-0.2 |
| FB6E | SrO6Fe2O3 | 380+/-10 | 3.80+/-10 | 290.5+/-11.9 | 3.65+/-0.15 | 393.9+/-11.9 | 4.95+/-0.15 | 27.5+/-1.6 | 3.45+/-0.2 |
| FB5N | SrO6Fe2O3 | 440+/-10 | 4.40+/-10 | 256.8+/-11.9 | 2.85+/-0.15 | 2259.2+/-11.9 | 2.88+/-0.15 | 36.7+/-1.6 | 4.6+/-0.2 |
| FB5B | SrO6Fe2O3 | 420+/-10 | 4.20+/-10 | 262.6+/-11.9 | 3.3+/-0.15 | 266.6+/-11.9 | 3.35+/-0.15 | 33.4+/-1.6 | 4.2+/-0.2 |
-
Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets IEC Standard (IEC 60404-8-1)
| Grade | Remanence Br | Coercive Force Hcb(Hc) | Intrinsic Coercivity Hcj(Hci) | Max. Energy Product (BH)max | ||||
| mT | kGs | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | kOe | KJ/m³ | MGOe | |
| HF8/22 | 200/220 | 2.00/2.20 | 125/140 | 1.57/1.76 | 220/230 | 2.76/2.89 | 6.5/6.8 | 0.8/1.1 |
| HF20/19 | 320/333 | 3.20/3.33 | 170/190 | 2.14/2.39 | 190/200 | 2.39/2.51 | 20.0/21.0 | 2.5/2.7 |
| HF20/28 | 310/325 | 3.10/3.25 | 220/230 | 2.76/2.89 | 280/290 | 3.52/3.64 | 20.0/21.0 | 2.5/2.7 |
| HF22/30 | 350/365 | 3.50/3.65 | 255/265 | 3.20/3.33 | 290/300 | 3.64/3.77 | 22.0/23.5 | 2.8/3.0 |
| HF24/16 | 350/365 | 3.50/3.65 | 155/175 | 1.95/2.20 | 160/180 | 2.01/2.26 | 24.0/25.5 | 3.0/3.2 |
| HF24/23 | 350/365 | 3.50/3.65 | 220/230 | 2.76/2.89 | 230/240 | 2.89/3.01 | 24.0/25.5 | 3.0/3.2 |
| HF24/35 | 360/370 | 3.60/3.70 | 260/270 | 3.27/3.39 | 350/360 | 4.40/4.52 | 24.0/25.5 | 3.0/3.2 |
| HF26/16 | 370/380 | 3.70/3.80 | 155/175 | 1.95/2.20 | 160/180 | 2.01/2.26 | 26.0/27.0 | 3.2/3.4 |
| HF26/18 | 370/380 | 3.70/3.80 | 175/190 | 2.20/2.39 | 180/190 | 2.26/2.39 | 26.0/27.0 | 3.3/3.4 |
| HF26/24 | 370/380 | 3.70/3.80 | 230/240 | 2.89/3.01 | 240/250 | 3.01/3.14 | 26.0/27.0 | 3.3/3.4 |
| HF26/26 | 370/380 | 3.70/3.80 | 230/240 | 2.89/3.01 | 260/270 | 3.27/3.39 | 26.0/27.0 | 3.3/3.4 |
| HF26/30 | 385/395 | 3.85/3.95 | 260/270 | 3.27/3.39 | 300/310 | 3.77/3.89 | 26.0/27.0 | 3.3/3.4 |
| HF28/26 | 385/395 | 3.85/3.95 | 250/265 | 3.14/3.33 | 260/275 | 3.27/3.45 | 28.0/30.0 | 3.5/3.8 |
| HF28/28 | 385/395 | 3.85/3.95 | 260/270 | 3.27/3.39 | 280/290 | 3.50/3.60 | 28.0/30.0 | 3.5/3.8 |
| HF30/26 | 395/405 | 3.95/4.05 | 250/260 | 3.14/3.33 | 260/270 | 3.27/3.39 | 30.0/31.5 | 3.8/3.9 |
| HF32/17 | 410/420 | 4.10/4.20 | 160/180 | 2.01/2.26 | 165/175 | 2.07/2.20 | 32.0/33.0 | 4.0/4.1 |
| HF32/22 | 410/420 | 4.10/4.20 | 215/225 | 2.70/2.83 | 220/230 | 2.76/2.89 | 32.0/33.0 | 4.0/4.1 |
| HF32/25 | 410/420 | 4.10/4.20 | 240/250 | 3.01/3.14 | 250/260 | 3.14/3.27 | 32.0/33.0 | 4.0/4.1 |
04. SI and CGS Unit Conversion for Magnetism Quantity
| Quantity | Symbol | SI Unit | CGS Unit | Unit Conversion |
| Remanence | Br | T | Gs | 1T=10kGs |
| Coercive Force | Hcb | kA/m | Oe | 1kA/m=4πOe≈12.57Oe |
| Intrinsic Coercivity | Hcj, iHc | kA/m | Oe | 1kA/m=4πOe≈12.57Oe |
| Max. Energy Product | BHmax | kJ/m3 | MGOe | 1kJ/m3=4π/102MGOe≈0.126MGOe |
| Magnetic Flux | Φ | Wb,Vs | Mx | 1Wb=1Vs=108Mx |
| Magnetization Intensity | M | T | Gs | 1T=10kGs |
| Magnetic Field Intensity | H | kA/m | Oe | 1kA/m=4πOe≈12.57Oe |
| Magnetic Induction Intensity | B | T | Gs | 1T=10kGs |
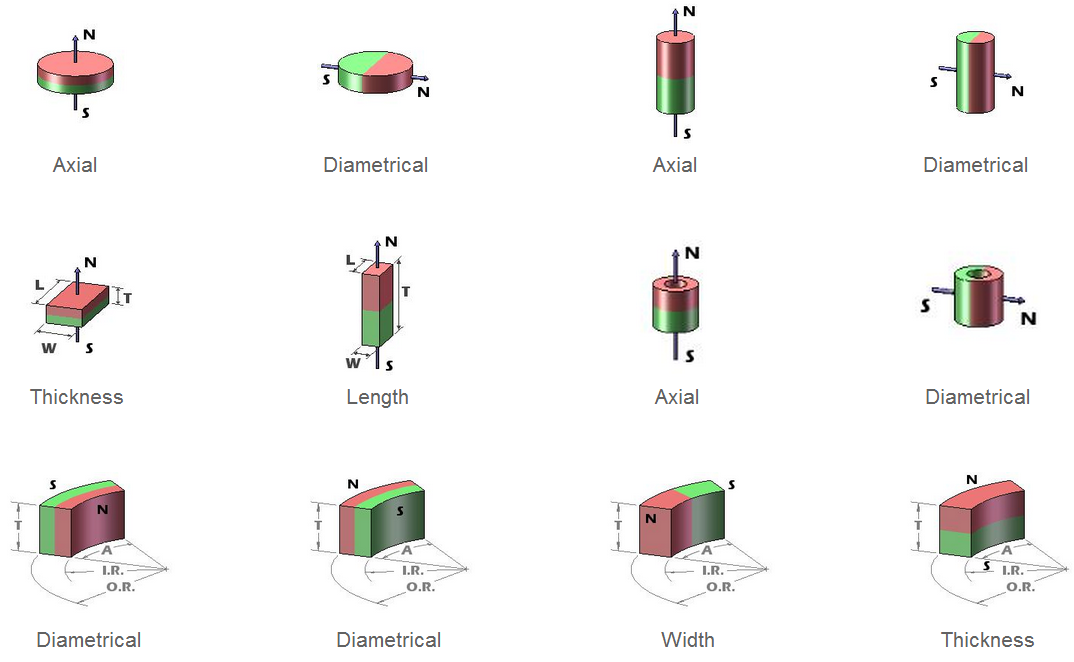
05. Ferrite (Ceramic) Magnets Magnetization Directions
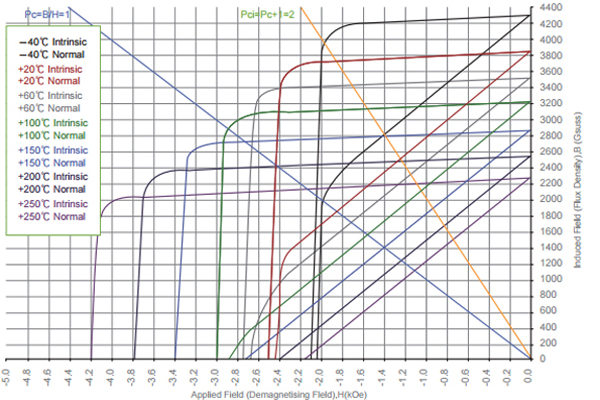
06. Physical Properties of Ferrite Magnets
| Curie Temperature (°C) | 450 |
| Maximum Operating Temperature (°C) | 250 |
| Hardness (Hv) | 480-580 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 4.8 - 4.9 |
| Relative Recoil Permeability (μrec) | 1.05 - 1.20 |
| Saturation Field Strength, kOe (kA/m) | 10 (800) |
| Temperature Coefficient of Br (%/°C) | -0.2 |
| Temperature Coefficient of iHc (%/°C) | 0.3 |
| Tensile Strength (N/mm) | <100 |
| Transverse Rupture Strength (N/mm) | 300 |
08. Permanent Magnets Comparison
| Permanent Magnets | (BH)max (MGOe) | Curie Temperature (°C) | Max. Working Temp. (℃) | Anti-corrosion | Machinability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintered NdFeB Magnets | 27-52 | 310-370 | 80-230 | Bad | Normal |
| AlNiCo Magnets | 1.1-11.5 | 890 | 500 | Good | Fair |
| SmCo5 | 14-25 | 750 | 250 | Good | Normal |
| Sm2Co17 | 22-32 | 800-840 | 350 | Good | Normal |
| Ferrite Magnets | 0.8-5.3 | 450 | 250 | Good | Normal |
| Bonded NdFeB Magnets | 3-12 | 350 | 160 | Good | Good |
09. Ferrite (ceramic) Magnets Shipping Methods

(TNT, DHL, FedEx, UPS, etc), Air, Sea.
a: If the weight is under 40kgs, we recommend to send it in shielding boxes by Express.
b: If the weight is between 40-100kgs, it can be sent by Express or Air.
c: If the weight is over 100kgs, we recommend to ship them by Sea.
For more details about ferrite (ceramic) magnets, please send message to us or email to sales@sinnyuan.com. We will reply to you as early as possible.